 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Categories
Blog
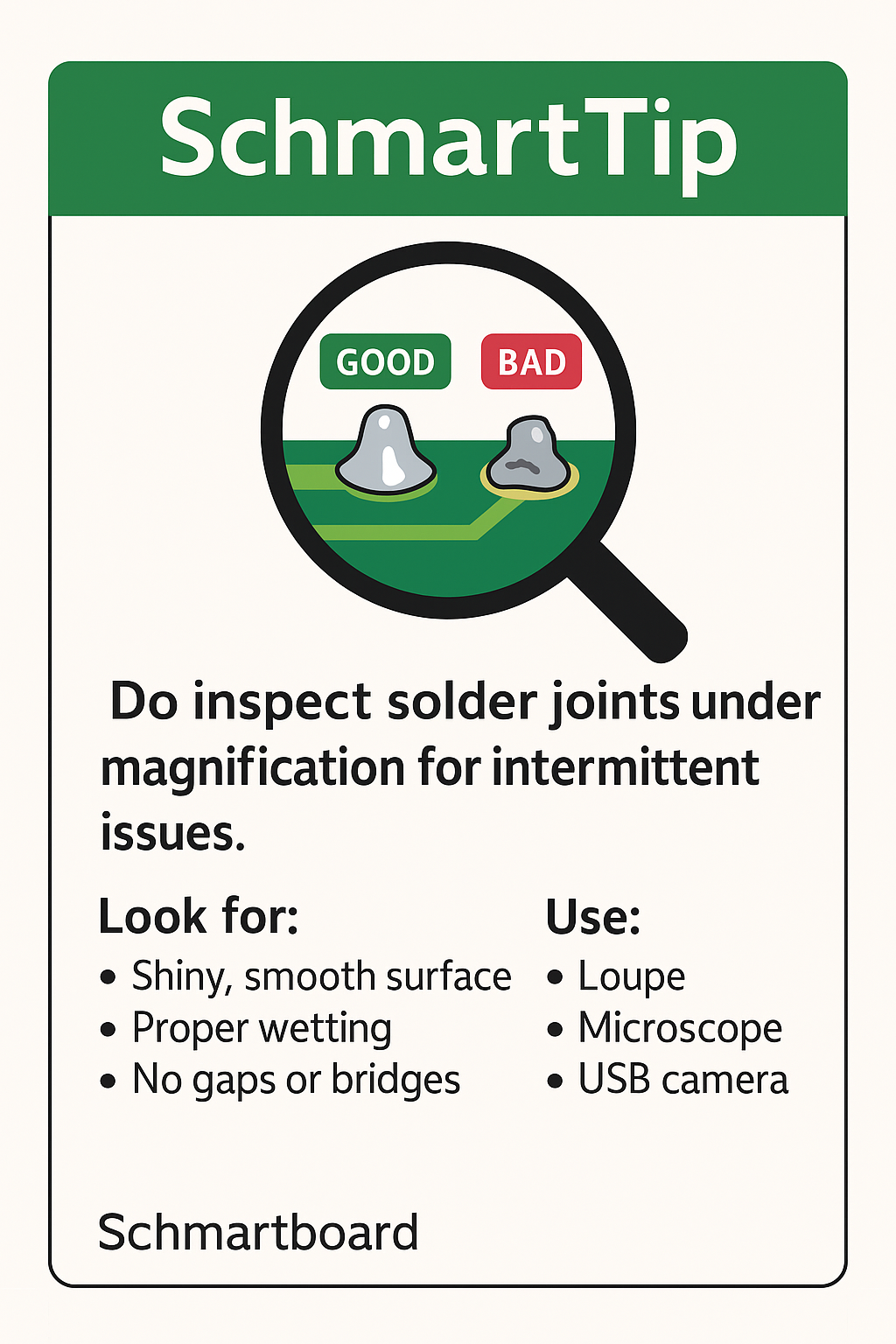
Do Inspect Solder Joints Under Magnification for Intermittent Issues
Posted by Schmartboard on Oct 26th 2025
A circuit is only as reliable as its connections — and in electronics, that means solder joints. Even the most perfectly designed PCB can fail if a single solder joint is cracked, cold, or barely making contact. The problem? Many of these flaws are too small to see with the naked eye.
That’s why one of the most important quality checks you can do is simple but powerful:
Do inspect solder joints under magnification for intermittent issues.
Why Magnification Matters
Solder joints are deceptively small. They might look fine under room lighting, but microscopic imperfections can lead to:
-
Intermittent connections — circuits work one moment, fail the next.
-
Open circuits — solder didn’t fully wet the pad or lead.
-
Cold joints — dull, grainy solder caused by insufficient heat.
-
Bridged pins — tiny solder blobs connecting adjacent pads.
-
Cracked joints — stress fractures that develop over time.
Magnification allows you to see the truth — the difference between a shiny, properly wetted joint and a weak one waiting to fail.
How to Inspect Solder Joints Properly
Here’s what to look for when using magnification tools such as a loupe, microscope, or USB inspection camera:
-
Shiny, smooth surface:
A good solder joint should have a concave, mirror-like finish — not dull or grainy. -
Proper wetting:
The solder should smoothly flow from the component lead to the pad, forming a natural curve. -
No gaps or voids:
Any visible cracks, pits, or voids indicate poor soldering. -
No bridges:
Adjacent pads or leads should not be connected by stray solder. -
Consistent size and shape:
Joints should appear uniform — uneven joints suggest inconsistent heat or solder volume.
Tools That Make Inspection Easier
-
10x–20x Jeweler’s Loupe: Portable and inexpensive for quick checks.
-
Digital USB Microscope: Allows high magnification and image capture for documentation.
-
Stereo Microscope: Ideal for rework stations and professional inspection.
-
Ring Light or Adjustable LED: Proper lighting reveals flaws you’d otherwise miss.
Common Causes of Bad Solder Joints
-
Insufficient or uneven heating.
-
Dirty pads or oxidized leads.
-
Using the wrong solder alloy or flux.
-
Moving the joint before cooling.
-
Excessive solder that bridges leads.
Recognizing these during inspection helps you correct the technique before problems repeat.
How Schmartboard Makes It Easier
At Schmartboard, we understand that soldering precision can make or break a project — especially for beginners or small-batch engineers. That’s why our Schmartboard prototyping products are designed to help you solder cleanly, consistently, and confidently.
-
Our patented “EZ” solder technology includes pre-tinned pads and raised traces, guiding solder flow automatically.
-
Ideal for SMD components, even under magnification — the joints form neatly with minimal effort.
-
You can focus on inspection and testing rather than rework and frustration.
When paired with proper inspection habits, Schmartboard helps you build professional-quality circuits right on your workbench.
Final Thoughts
Small defects cause big headaches. An intermittent connection can waste hours of debugging and lead to unreliable products in the field.
So before you power up your next board, take a moment to inspect those solder joints under magnification. It’s one of the fastest, easiest ways to ensure long-term reliability — and it’s a habit that separates careful engineers from careless ones.
Good connections are built, not guessed. Inspect, verify, and trust your work — the Schmartboard way.
Don’t Assume Power Supplies Are Perfectly Clean
In electronic circuit design, power is everything. Without a stable power source, even a well-designed circuit can behave unpredictably. But here’s a mistake many beginners—and even experienced designers—often make: Don’t assume your power supply is perfectly clean. Even regulated power supplies introduce noise, ripple, and voltage fluctuations that can interfere with your circuit’s performance. Ignoring power quality [...]
Do Choose the Right PCB Stack-Up Early to Support Signal Integrity
When designing a printed circuit board (PCB), it’s easy to jump straight into component placement and routing. But before you lay down a single trace, there’s one foundational decision that determines the success of your entire design: Your PCB stack-up. The stack-up refers to how the layers of your PCB are arranged — signal layers, power planes, [...]
Do Route High-Frequency Signals with Controlled Impedance
When working on high-speed or RF (radio frequency) circuits, your PCB traces are no longer just simple wires — they become transmission lines. And at that point, impedance control is essential for ensuring signal integrity, preventing reflections, and maintaining reliable performance. If you’re designing for USB, HDMI, Ethernet, DDR memory, or any fast digital interface, you [...]
Don’t Overcrowd the Board — Leave Room for Debugging
When designing a printed circuit board (PCB), it’s tempting to use every bit of available space. After all, shrinking the board size can reduce costs and make your design look sleek and efficient. But here’s the reality: overcrowding your board is a recipe for frustration when it comes time to test, debug, and modify your [...]
Understanding the Importance of Using a Ground Plane to Minimize Noise in PCB Design
When designing printed circuit boards (PCBs), there are numerous considerations that can significantly impact the performance and reliability of your circuit. One of the most vital yet often overlooked aspects is the use of a ground plane. Proper grounding strategies can reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), minimize noise, and improve signal integrity — especially in high-frequency [...]
Do Check Datasheets for Every Component
Do Check Datasheets for Every Component When designing a printed circuit board (PCB), every successful project starts with one thing: understanding your components. And there’s no better way to do that than by reading the datasheet. Skipping this step can lead to design flaws, unexpected performance issues, and costly rework — things we all want to avoid. At [...]
Don’t Cross Analog and Digital Grounds Carelessly
When designing mixed-signal PCBs that include both analog and digital components, one of the most common pitfalls is mishandling ground planes. At first glance, it may seem intuitive to separate analog and digital grounds completely — but doing so without careful consideration can create more problems than it solves. Why Grounding Matters Digital circuits are noisy by [...]
Do Label All Components and Nets Clearly: A Schmartboard Tip
In the world of electronics design, clarity is everything. Whether you’re prototyping on a breadboard, working on a Schmartboard, or finalizing a PCB for production, one of the most overlooked yet critical steps in the design process is properly labeling your components and nets. This small habit can save you from big headaches later. Why Labeling [...]
Don’t Use Components Without Understanding Their Limitations
When working with electronics, one of the biggest mistakes beginners (and even some experienced builders) make is using components without truly understanding their limitations. Whether you’re working with an integrated circuit (IC), a capacitor, or a diode, every part has thresholds—voltage, current, temperature, tolerance—that must be respected. Ignoring these limits doesn’t just risk a failed [...]
Recent Posts
- » Do Inspect Solder Joints Under Magnification for Intermittent Issues
- » Don’t Assume Power Supplies Are Perfectly Clean
- » Do Choose the Right PCB Stack-Up Early to Support Signal Integrity
- » Do Route High-Frequency Signals with Controlled Impedance
- » Don’t Overcrowd the Board — Leave Room for Debugging